Why should we suffer pain?
Kidney stones are the most painful conditions that a patient suffer due to the disorder found in the urinary system. Various studies indicate a significant rise in the prevalence of kidney stones with at least 12 percent of our population reported to be susceptible to urinary stones. Of which, 50 per cent of them are at high risk of renal damage, which can even lead to kidney failure. Generally, stone forms in the kidney, bladder and in the urinary tract.
What can a bean-shaped small organ do in our body, is miraculous. Despite weighing less than 190 gm, major functions of the bean-shaped organ is priceless such as filtering blood and excreting various wastes from the body along with controlling body-fluid levels. Urination is an important waste excretion process in which kidneys play a pivotal role. Any obstruction in which can lead to serious health issues. Kidney stone is the most prevalent condition found in urinary system which also called renal calculi or nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis.
Causes of stone deposit in kidneys
These stones are hard deposits made up of minerals that form inside your kidneys when they fail to function properly. These stones develop when the level of crystal-forming substances, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, exceed the level than the fluid in the urine can dilute. At the same time, your urine may lack substances that prevent crystals from concentrating, creating an ideal environment for kidney stones to form. Stones often form when the urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals to crystalize and stick together. Several factors contribute to the formation of kidney stones among which are diet, excess body weight, some medical conditions, and certain supplements and medications. While kidney stones usually found in the urinary tract including kidneys and bladder they can also form in gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary gland that tend to gradual failure of the affected organ.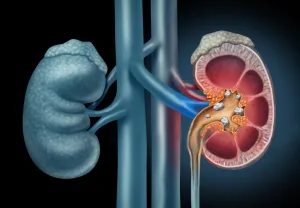
Pain over pain is the symptom
Kidney stones are often synonymous with pain as it is common seeing people with kidney stones suffering from intense pain. Abdominal pain starting from below the ribs and radiates to the groin is a primary symptom of this disorder. A kidney stone does not cause symptoms until it moves into you’re the ureter, a tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder. When deposits in the ureters, stone may block the urine flow, causing the kidney to swell and the ureter to spasm. As a result, one may experience severe pain or burning sensation during urination.
Kidney stones are in various types
Generally kidney stones are calcium stones, in the form of calcium oxalate that are more common and sometimes as calcium phosphate. Oxalate is produced by the liver every day or absorbed from your diet. Hence, diet having high oxalate content can increase the risk of stones. Certain fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts and chocolate, have high oxalate content. Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, intestinal bypass surgery and several metabolic disorders can increase the concentration of calcium or oxalate in urine.
Whereas, Calcium Phosphate stones are more common in metabolic conditions, such as renal tubular acidosis. It may also be associated with certain medications used for treating migraines or seizures, such as topiramate (Topamax, Trokendi XR, Qudexy XR).
A urinary tract infection often lead to the formation of struvite stones, which grow quickly than the former and become quite large, sometimes symptom manifestation is very low in this case.
Uric acid stones are another type that can form due to the losing of more fluid in some chronic diarrhoea conditions. Those who eat a high-protein diet, and those with diabetes or metabolic syndrome are prone to this condition. Certain genetic factors may also increase your risk of uric acid stones.
Gallbladder Stones 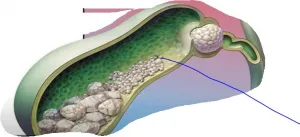
Our gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath the liver. The gallbladder carries a digestive fluid called bile that is secreted to the small intestine. Hardened deposits of this digestive fluid in the gallbladder is later developed as gallstone.
People experience intensive pain in the lower back or abdomen are advised to consult a doctor which may be a general symptom of this disease. Excess of cholesterol and bilirubin are contributed to the growth of gallstones.
Two types of gallstones are found in gallbladder that are cholesterol gallstones and pigment gallstones. The former is the most common type of gallstones, often appears in yellow colour. Chiefly, these gallstones are composed by undissolved cholesterol, though may contain other components as well.
While pigment gallstones are formed when your bile contains too much bilirubin and found in dark brown or black colour.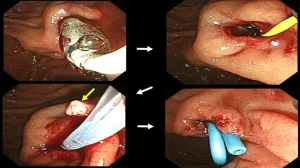
Pancreatic Stones
The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach, close to the duodenum. They produce insulin and enzymes to help digest the food. Pancreatitis occurs when these enzymes damage the intestine.
There are acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis is a sudden and severe inflammation of the pancreas. It can occur when digestive enzymes become activated within the pancreas instead of the small intestine, leading to the pancreas digesting itself. Chronic Pancreatitis: Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term inflammation of the pancreas that can lead to permanent damage and impairment of the organ’s function.
Pancreatic stones are formed due to many reasons including block in the pancreatic duct, calcium or mineral metabolism, alcohol use and gallstones. Sometimes medicine induced side-effects can also be a reason of pancreatitis.
Symptoms
Unlike to other stone diseases pancreatitis manifest more symptoms. Despite heavy pain in the upper abdomen spreading towards the back, fever, high heartbeat, swollen abdomen, and diarrhoea. Patient with pancreatitis experience gradual weight loss.
Salivary Gland Stones
Sialolithiasis or Salivary Gland Stones are small, hard crystallized minerals that form within the duct of the salivary glands. Salivary glands secret saliva, that has several functions including facilitating the digestion. Salivary gland stones can obstruct the flow of saliva, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. It is commonly found in middle age adults.
Causes
Causes may vary including drug induced side-effects, dehydration and mineral build-up are commonly identified reasons.
Symptoms
Pain in the face, mouth, and neck that worsens while taking substances into the mouth or swallow, foul taste in mouth and redness over the affected area are major symptoms.
Gallbladder stones may lead to potential damage in the salivary gland and experience difficulty in eating or speaking.
Diagnosis and Treatment 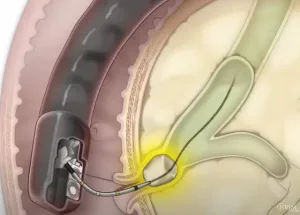
Diagnosing a stone begins with a physical examination and imaging tests such as high-resolution CT scan or X-ray from the kidneys to the bladder. It helps to identify the size of the stone.
Treatment depends on the size of the stone, surgery is prescribed if it is big in allopathic medicine. Small stones can be removed through medication. In homoeopathy, size of the stone does not change the treatment method as it can be removed through medication lasting three months