Does fibroadenoma cause breast cancer?
This is a very common concern, almost all women share with fear shall be addressed here in detail to expunge all your doubts regarding fibroadenoma and allied cancer. Given that breast cancer is one of the leading cancers in India, people especially young women worry about ‘fibroadenoma can cause cancer’. As we understand, cancer is a terminal illness that too brings suffering despite the economic burden it imposes upon the diseased and their loved ones due to the expensive method of treatment and medicine shortage, which certainly force people to lead a dreadful life. Despite these facts, you need not to worry about fibroadenoma. You may have many questions about this human phenomena vis-à-vis what is fibroadenoma, to its causes, to treatment and to potential side effects so on and so forth. This article will meticulously deal with it by analyzing various aspects of fibroadenoma.
Fibroadenoma, fear what you don’t know!
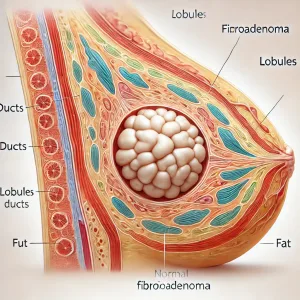
We need to understand first that fibroadenoma is a most common form of non-cancerous breast lump found in women. A fibroadenoma is a solid lump, not filled with fluid, made up of both glandular tissue and stromal tissue found in breasts that shows it is not typically dangerous as most of the women are scared, unless it grows in size over a period. The fibroadenoma is normally painless when you touch or squeeze it, but it may be painful at times then needs treatment.
Origin of the word ‘Fibroadenoma’
If we dig out the etymology of fibroadenoma, we then find as the name indicates fibroadenoma is a combination of two words, namely fibroma and adenoma. The former term denotes a non-cancerous tumor from connective tissues known as fibrous tissues whereas the latter signifies a benign epithelial tumors originating from glandular tissue.
Is fibroadenoma cancerous? Does it increase the risk of cancer
Simple fibroadenoma usually does not increase the risk of breast cancer. However, complex fibroadenomas may increase the risk slightly because this type of lesion may contain calcified breast tissue than the former which warrants a frequent physical observation of breast from our side. According to an estimation 10 percent of the world’s female population suffers from fibroadenoma once in a lifetime. Even if fibroadenomas are non-cancerous whether it is simple or complex, homeopathic systems claim complete cure through medicines. Fibroadenoma tends to occur in early life of women mostly in adolescent girls and less common in women experiencing postmenopausal condition. The incidence of fibroadenoma decreases with increasing age and is generally found in females before 30 in the general population. However, fibroadenoma at its early stage can easily curable, so you need not to worry about cancer.
Do you know the causes of fibroadenoma?
Experts in this field did not trace the precise reasons behind fibroadenoma so as to the causes are debated among scientists. However, they strongly believe in hormonal etiologic theory which says estrogen plays a crucial role in the later development of fibroadenoma because the lesion has a hormonal etiology associated with the increased sensitivity of breast tissue to estrogen, the female reproductive hormone. As a result, fibroadenoma grows during pregnancy when estrogen levels are higher and tends to contract during menopause when estrogen levels are lower. There may also be genetic causes but some studies point out that women who had oral contraceptives before 20 years of age incline to suffer from fibroadenoma at higher rates than others. So beware of loose use of oral contraceptives at younger age.
How it looks- like?
Fibroadenoma tends to be round or oval or flat like a coin and mostly have well-defined borders. This painless lump is a mass consisting of both epithelial and stromal tissues located under the breast skin. It can often feel like a marble within the breast. It has a characteristic of easy moving like a mouse as against to being stuck in one place that owes another name for it, breast mice!
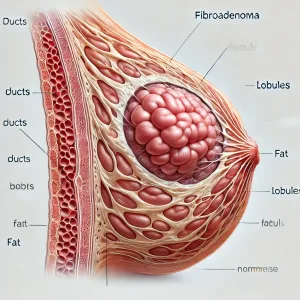
Tumors are always huge?
When we talk about tumors, often huge swellings come scaring to our mind. Whereas, these firm, rubbery masses of fibroadenoma is often in the size up to 2.5 centimeters that is to say about an inch in diameter. Simple fibroadenomas are the most common type. They stand smaller and the cells appear the same throughout the tissue. However, the size of a fibroadenoma may double over time growing up to five centimeters. At the same time, larger seized fibroadenoma has calcifications or cysts, called complex fibroadenoma found in women older than 35. Fibroadenomas, bigger than five centimeters, are categorized as giant fibroadenomas. Over time, it may even shrink and disappear as estrogen level decreases.
Are young women more prone to fibroadenoma?
Fibroadenoma are most likely to develop in women between the ages of 20-35 but also found in any group. It is less common among postmenopausal women due to the shrinking of the lumps followed by the menopause. Although anyone who is menstruating can develop a fibroadenoma. As we said early, when estrogen levels are higher fibroadenoma tends to grow and when estrogen levels are lower it contracts. Hence, it is found more commonly in young women. Fibroadenomas are most likely to develop in women between the ages of 20 and 35, although they can occur in any age group. They are less common among postmenopausal women, as the lumps tend to shrink following menopause. However, anyone who is menstruating can develop fibroadenoma. As mentioned earlier, fibroadenomas tend to grow when estrogen levels are higher and contract when estrogen levels are lower. This is why they are more commonly found in younger women.
How can it be diagnosed?
As we say ‘never ignore symptoms’ that our body experiences, a similar health advice is that bodily sensations may be the harbinger of potential health issues. Hence, observing bodily changes is a crucial step in preventing imminent diseases which is applicable to the breasts as well. Self-monitoring of the breasts on a regular basis is the best way to the early identification of the unusual growth of fibroadenoma. If you feel a lump, don’t worry, examine it closely for a certain period. If you notice any harmful stimuli, consult with a doctor who may recommend any of the available tests if necessary followed by a physical examination. Early detection and medication can eliminate harmful fibroadenomas. The diagnosis often tend to vary depending on the complexity of the condition and the age of the experiencing person. Tests like imaging test such as a mammogram or ultrasound possibly prescribed to a younger age woman by passing there of sound waves. Ultrasound is said to differentiate solid portions from the cystic masses easily. Whereas mammograms are used to assess volume of the masses in women over 35 years with the help of X-rays.
Now you need to think about treatment
Small fibroadenomas can easily be combated by taking medicines even if there is a chance to shrink on their own over the period. A doctor may recommend regular monitoring of this to identify the changes occurring in both lump and breast for a certain period of time. You need not undergo surgery if the lump is in an early stage and if you are worried about future growth in breasts, advised to take medicines and get cured before it worsens. However, if it causes a change in the shape of the breasts or continues to grow due to excessive lumps, doctors might recommend medicines. Even though surgery is a most common medical practice to remove it, nowadays it can also be treated by administering medication instead of undergoing surgical method that may lead to breast deforming.
Breast surgery is unthinkable
Since many women consider breasts to be an integral part of womanhood, the breast deformation due to surgery worries them and they are deterred from undergoing the surgery. As we stated earlier, in most cases, fibroadenoma can be treated easily. Allopathic systems recommend surgery if they cause compression of adjacent breast tissues or bigger than 2.5 cm in size. Apart from the surgical procedures used in the allopathic system, it can be cured completely through medication in homeopathy.